




It was named after ergothioneine, which was first isolated in 1909 by French pharmacist Charles Tanret from the ergotham fungus that destroys black grains.
At present, it has been found that it can be synthesized in most fungi, some mushrooms, streptococcus, mycobacterium and other microorganisms. Animals, plants and humans cannot synthesize this substance independently, but need to obtain it through diet.
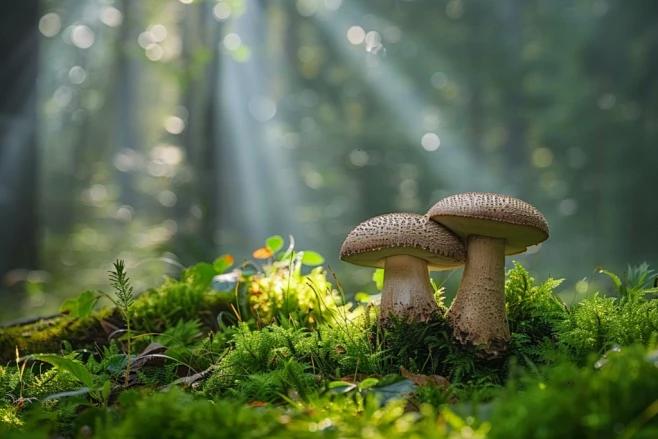
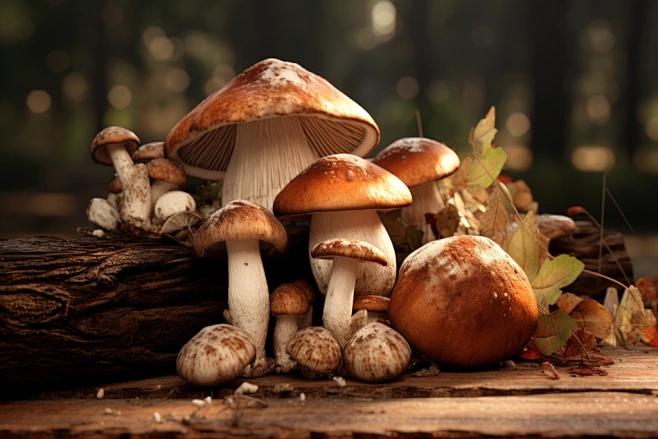


In everyday life, ergothioneine is found in the highest amounts in mushrooms. Ergothioneine is mainly found in certain fungi and bacteria, and mushrooms are the most abundant and easily available source for most people.
Mushrooms are the most concentrated dietary source of this amino acid —— hundreds of times higher than any other food. However, the amount of ergothioneine depends on the type of mushroom.
Gray oyster mushroom (Pleurotus citrinopileatus): 10-65 mg/g on dry basis
Lagunculus edulis (Boletus edulis): 7+ mg/g on dry basis
Mushroom (Lentinula edodes): About 1 mg/g on dry basis
Enoki: fresh contain 353 mg/100g.
While mushrooms are the main source of ergothioneine, other foods contain this compound, though usually in much lower amounts:


Black and red beans: Famous for their antioxidant properties, they also provide a moderate amount of ergothioneine.
Oats: A staple breakfast food, oats contain ergothioneine, which adds to their image as a heart-healthy food.
It shows good stability at high temperature or different pH values.
At pH value of 7.0, it has a high standard REDOX potential and can effectively protect cells.
In the condition of strong alkali, ergothioneine can maintain good stability and effectively inhibit the oxidation of metal ions.
Solubility:Easily soluble in water, soluble in methanol and ethanol.
EGT (ergothioneine) is transported to the mitochondria, an important "energy factory" of life activities, through OCTN1 transport protein on the cell membrane and mitochondrial membrane.
At the same time, it has the ability to remove free radicals, reduce lipid peroxidation and promote the body's own antioxidant enzymes. In terms of antioxidant, EGT is a powerful player.
Powerful Antioxidant
due to its unique sulfur-containing imidazole ring. Ergothioneine's stability and ability to target specific cellular regions make it a particularly effective scavenger of harmful free radicals.
Anti-inflammatory action
Because of its anti-inflammatory properties, ergothioneine can inhibit inflammatory pathways and reduce the risk of chronic inflammation, thus helping to prevent a variety of chronic diseases.
Anti-aging effect
By protecting cells from oxidative stress and inflammation, ergothioneine helps slow the aging process and prolong the healthy life span of tissues and organs.
Neuropathy Protection
S-amygdalin has neuroprotective properties that can prevent the development of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease.
Immunoregulation
Methionine helps maintain an environment conducive to an effective immune response by enhancing the function of the immune system and reducing oxidative stress and inflammation.
Support Cardiovascular Health
Studies have shown that ergothioneine is associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality, especially in long-term follow-up studies.

Interested in our supplements? Get your personalized quote now!
 Call us on:
Call us on:  Email Us:
Email Us:  Office Add:
Office Add: