



In 1936, Hungarian physiologist Szent Gyorgyi (Szent Gyorgyi) discovered an antioxidant substance that can improve the strength of capillaries and normalize their permeability. Scientists classified it as a vitamin P group.
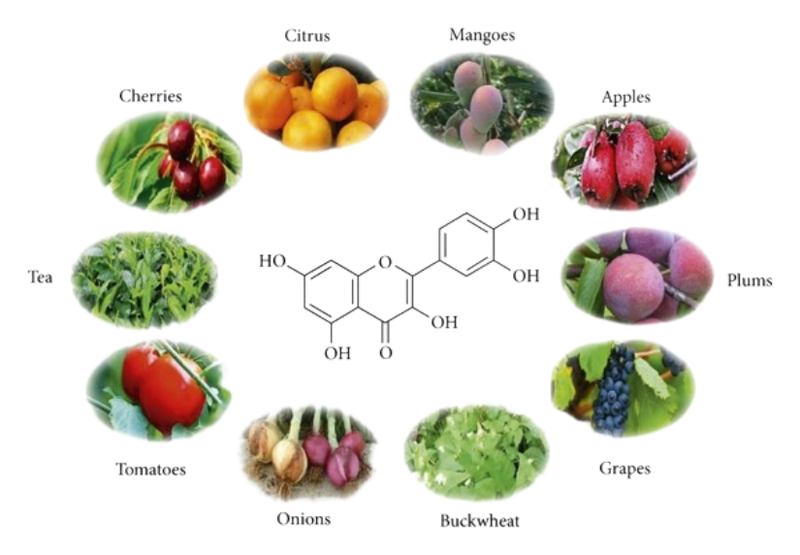
Quercetin is widely found in the bark, flowers, leaves, buds, seeds and fruits of many plants, mostly in the form of glycosides, such as rutin, quercetin, gentiana glycoside, etc., which can be obtained by acid hydrolysis.
Among these, the content is particularly high in buckwheat stalks and leaves, sea buckthorn, hawthorn, and onions. Quercetin is also found in a variety of foods, including onions, scallions, asparagus, cabbage, mustard greens, green peppers, chicory, grapefruit, lettuce, hawthorn, apples, mangoes, plums, radishes, blackcurrants, potatoes, and spinach.
Dihydroquercetin, also known as taxifolin, is a white needle-like crystal with a melting point of 240-240℃. It is . Taxifolin is a bioflavonoid extracted from the roots of larch trees in cold regions and is an essential natural antioxidant for the human body.
Dihydroquercetin and Quercetin are flavonoids belonging to the same plant.
| Quercetin | Dihydroquercetin |
| Soluble in methanol, ethyl acetate, glacial acetic acid, pyridine, acetone, etc., insoluble in water, benzene, ether, chloroform, petroleum ether, etc. | Easily soluble in ethanol and acetic acid, slightly soluble in cold water, and almost insoluble in benzene. |
|
|
Source:
Quercetin is widely found in the bark, flowers, leaves, buds, seeds and fruits of many plants. It is also found in common foods such as Onions, potatoes and apples. It is usually used as a dietary supplement or food additive.


Dihydroquercetin: Content of dihydroquercetin is low in plants, generally 2~3%, mainly from larch, cypress and other pine plants. Cypresses are mainly distributed in Siberia, Russia, and rarely in other areas.

Quercetin:
The metabolism of quercetin in human body is complicated, and the bioavailability is relatively low, which may be affected by intestinal microorganisms.
Dihydroquercetin:
Due to the structural changes, the absorption and metabolism of dihydroquercetin in vivo may be more convenient and the bioavailability may be higher.
- Antioxidant:
The mechanism of quercetin's antioxidant effect is mainly to remove free radicals and superoxide anions, which are mainly through three ways:
(1) It combines with superoxide anion to reduce the production of oxygen free radicals;
(2) Chelated with iron ions to prevent the formation of hydroxyl radicals;
(3) Aldehyde glucuronidase was inhibited to reduce the consumption of reduced coenzyme II (NADPH), thus improving the body's antioxidant capacity.
Antiviral effect Quercetin has inhibitory effect on herpes virus and influenza virus.
Anticancer activity Quercetin has anticancer properties against a variety of tumors, such as cervical cancer, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer and so on.
Protective effect of quercetin on hepatocyte damage induced by oxidative stress.
Cardiac protection effect Foreign scholar Chekalina observed 85 cases of coronary heart disease patients, quercetin treatment significantly reduced the number of ventricular premature beats, indicating that quercetin has a significant cardiac protective effect on coronary heart disease.
It protects the kidney
It protects the bone and joint
It protects the nerve
- Protective effect on the eyes and inhibits the formation of cataracts.
- Inhibiting cataract formation.
- Protecting diabetic retinopathy.

Interested in our supplements? Get your personalized quote now!
 Call us on:
Call us on:  Email Us:
Email Us:  Office Add:
Office Add: